Published 11 June 2020
New precautions in place due to COVID-19 have propelled us faster into the cashless economy. Learn why the future just might be cashless.
Going cashless during COVID-19
When we originally published this article in November 2018 during holiday shopping season, we could not have foreseen that a global health crisis would accelerate cashless payments worldwide. But new precautions in place due to COVID-19 have propelled us faster in the direction of contactless transactions everywhere.
Transmission of the disease from handling banknotes has consumers concerned, but the risk is reported to be low compared with touching credit card terminals and PIN pads. Yet the plexiglass that divides customer from cashier urges less reliance on bills and coins in favor of using point of sale machines to swipe your credit card.
Central banks around the world are taking steps to quarantine and sterilize banknotes to promote retained trust and universal acceptance of cash. Even so, many financial industry analysts are predicting that truly contactless payments through mobile e-wallets may be upon us sooner than previously forecast as consumers and retailers become more accustomed to eschewing cash.
Mobile payments are the future
According to Statista, 259 million Americans routinely bought products online in 2018.
That wasn’t the case just a few years ago when many of us were hesitant to punch in our credit card numbers to a website. But as ever more business is transacted online, financial services and “fintech” companies have built and continue to improve a secure payments ecosystem that consumers and businesses can be confident will protect their most vital assets: their private information and money.
Pretty soon we might not need to pull out a physical card as our credit card information gets linked with mobile payment systems. All you need is your finger, your phone, or a watch – items you probably already have on hand, literally. As more consumers adopt this convenience, “e-wallets” will eventually replace cash altogether.
The United States and Emerging Markets Lead
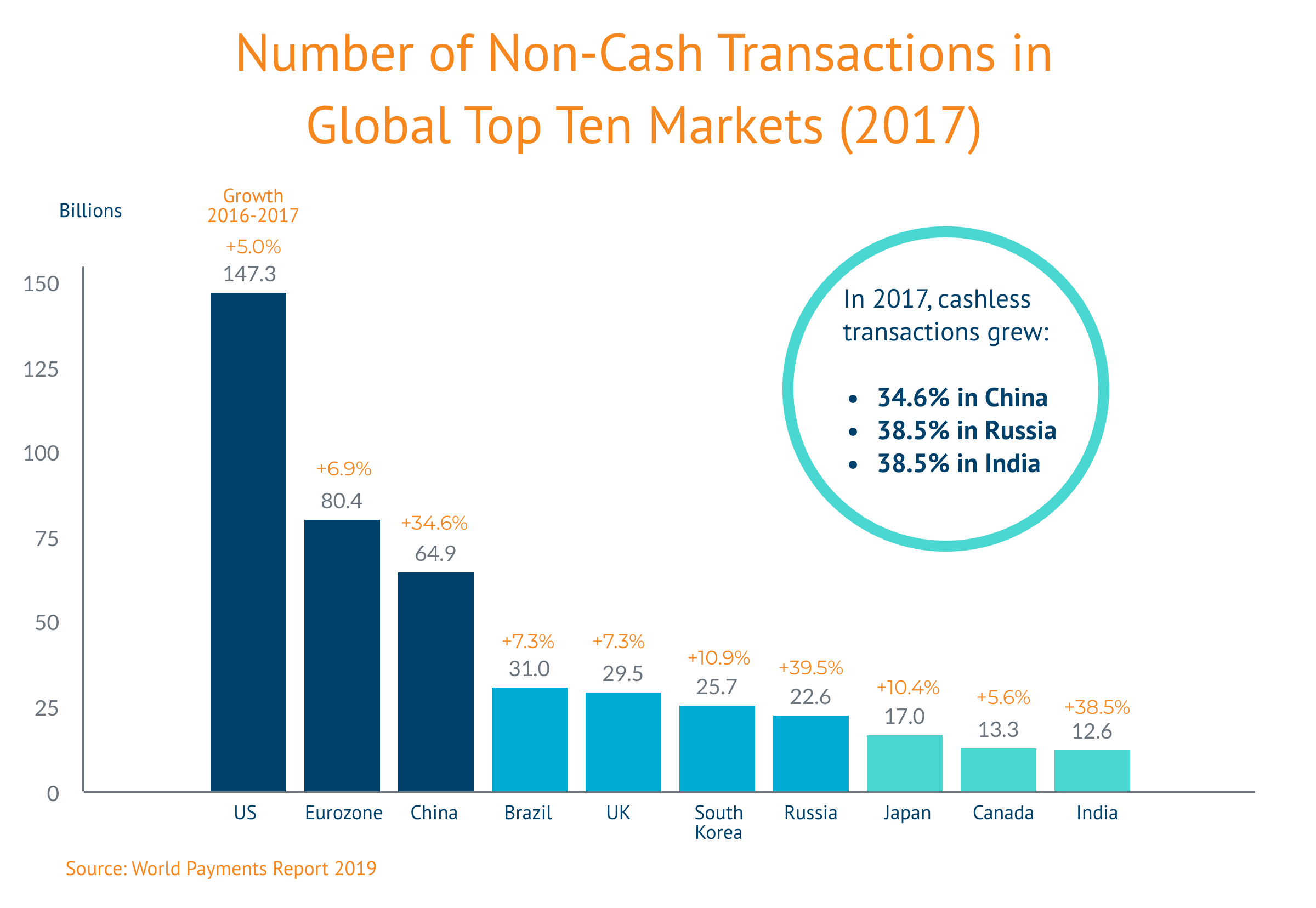
Mobile payments in the United States, China, Russia and India are driving the global trend – the United States by sheer volume of cashless transactions and the big emerging markets by virtue of how fast they are growing. In 2017, non-cash transactions grew 34.6 percent in China, 38.5 percent in Russia, and 38.5 percent in India.
Russia’s surge owes to the Central Bank of Russia’s implementation of a National Payment Card System that boosted growth of cashless transactions by 36.5 percent after it was introduced in 2015-2016. AliPay and WeChat Pay are keeping China on a sustained upward trajectory. Mobile payments in China climbed from US$2 trillion in 2015 to US$15.4 trillion in 2017, an amount greater than the combined total of the global transactions processed by Visa and Mastercard. India has improved its regulatory environment for digital payments as smartphone penetration expands.
Leapfrogging in developing countries
According to the 2019 World Payments Report, developing markets as a group contributed 35 percent of all non-cash transactions in 2017 and are close to reaching half of all non-cash transactions if they maintain the current rate.
Financial inclusion initiatives in developing countries that are designed to pull citizens into the formal banking system combined with an increase of mobile phone ownership means developing countries are leapfrogging over credit card use, going from cash to mobile payments.
Remittances, which comprise a high percentage of GDP in many developing countries, are being facilitated increasingly through person-to-person mobile money transfers. In one example, Western Union and Safaricom, a mobile provider in Kenya, have teamed to enable 28 million mobile wallet holders to send money to family and others over Western Union’s global network.
The Global Mobile Industry Association predicts the number of smartphones in use in sub-Saharan Africa will nearly double by 2025, enabling previously “unbanked” individuals to send and receive money by phone. For merchants in developing countries, scanning a QR code on a phone is faster and cheaper than installing point-of-service terminals that require a continuous electrical supply for reliability.

Mobile people with mobile phones
Chinese tourists are also driving global proliferation of mobile payments as vendors work to accommodate Chinese travelers in airports, restaurants, hotels, and stores. China’s Alipay advertised popular “outbound destinations without wallets” for Golden Week, when millions of Chinese go on vacation. Last year, prior to travel restrictions, there was a boom in Chinese tourists to Japan, with over 9.5 million visitors in 2019. China’s WeChat Pay teamed with Line, Japan’s popular messaging app service to offer mobile payments to Japanese retailers seeking to accommodate the influx of Chinese tourists. WeChat’s rival, Alipay, is also partnering to extend services in Japan.
Global standards and interoperability are needed
Through national financial inclusion programs, a steep increase in the accessibility of mobile phones, and with trade driving more global business transactions online, a cashless global economy could be in our future.
What’s standing in the way of faster integration globally of mobile payments, however, is a lack of international standards and common approaches to security, data privacy, and prevention of cybercrimes.
Companies in this space are continually evolving layers of protections such as the chips on your credit cards, encryption, tokens, and biometrics to stay ahead of cyber criminals, but it’s a constant battle against fraud and hacking of personal account information. For example, tokenization is a technology that safeguards bank details in mobile payment apps. That’s how Apple Pay works – rather than directly using your credit card details, your bank or credit card network generates random numbers that Apple programs into your phone, masking valuable information from hackers.
Differing national regulatory approaches to data authorization and distributed ledger technology (like blockchain) could fragment markets and inhibit adoption of the underlying technologies that permit mobile payments. Industry groups say international standards should be modernized to reflect technological innovations, but also harmonized to avoid developing different payments systems for different markets.
Interoperability is then the cornerstone of expanding trade through global digital payments. Groups like the PCI Security Standards Council advocate for international cooperation not only to set standards for ease of consumer use but because no single private company or government can stay continually ahead of hackers. They say that sharing information and best practices can raise everyone’s game, prevent attacks, and disseminate alerts quickly to stop the spread of damage when an attack occurs.
Mobile payments slim my wallet in more ways than one
By 2023, there will be three times as many connected devices in the world as there are people on Earth. (And that prediction was made pre-pandemic.) Young people with new spending power are favorably disposed to cashless transactions and shopping through their devices. Mobile payments help connect poorer and rural citizens to the formal economy just through SMS texts. Even tourism is spreading a culture of mobile payments. And many brick and mortar retailers say online browsing can drive in-store sales and help the bottom line.
Small businesses are making great use of mobile payment readers to take payments anywhere on the go, from selling jam at farmers markets to selling band t-shirts at small music venues. Business executives surveyed in the World Payments Report also cite increasing use of such rapid transfer payments to speed the settlement of business-to-business invoices and for supply chain financing, particularly across borders.
Experts are realistic, however, that cash isn’t dead yet. In most countries, cash payments as a share of total payment volume is declining, but cash in circulation is stable or rising – and that seems to be holding true despite the pandemic.
For a little while anyway, I conserved both cash and mobile spending during the pandemic. I’m back to routinely overspending at Starbucks where my thumb is all it takes to reload the card on the app using a preloaded credit card. If my behavior is any indication, the ease of mobile payments will probably cause many of us to spend more as the cash doesn’t have to physically leave the grip of our hands. The increase in availability and accessibility of cashless, mobile payments will be good for economic recovery and good for global trade.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in November 2018 and has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
© The Hinrich Foundation. See our website Terms and conditions for our copyright and reprint policy. All statements of fact and the views, conclusions and recommendations expressed in this publication are the sole responsibility of the author(s).




